C5 – Water supply industry and population connected to water supply industry in the Republic of Moldova
Is the percentage of Moldovan citizens with access to improved water supply services increasing?
Figure 1 - Population connected to water supply industry in the Republic of Moldova (2012-2016)
Data sources:
Population connected to water supply industry provided by Apele Moldovei of the Republic of Moldova
Note: Data in excel table was provided by the Apele Moldovei to the European Environment Agency under the ENI SEIS II East Project.
Figure 2- Development of net volume of water supplied by water supply industry and water losses during transport in the Republic of Moldova (2012-2016)
Data sources:
Losses during transportation provided by Statistical Databank of the National Bureau of Statistics of the Republic of Moldova
The main indicator of water use provided by Statistical Databank of the National Bureau of Statistics of the Republic of Moldova
The water supply industry is providing water to the public for various purposes, such as domestic use, drinking water, agriculture and industry.
In Moldova, 1.6 million inhabitants, 53 % of the total population, was connected to the public water supply system in 2016. The rest of the population met their water demand by self-supply. The water supply industry supplied 84.8 million m3 of water, which is equal to 10 % of the total annual freshwater abstraction in the country. As a result of the high pollution of surface water resources, the country is heavily dependent on groundwater resources, particularly for drinking purposes, which causes overexploitation of the groundwater resources (UNECE, 2014). On the other hand, because of the poor condition of the water supply system, almost half of the water supplied is lost during transport.
According to estimates, the percentage of the total population connected to the water supply increased by 11.1 % between 2012 and 2016. However, Moldova is still far from meeting target 6.1 of Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 6, which aims, ‘by 2030, to achieve universal and equitable access to safe and affordable drinking water for all’. Similarly, target 6.2 aims to, ‘by 2030, achieve access to adequate and equitable sanitation and hygiene for all and end open defecation, paying special attention to the needs of women and girls and those in vulnerable situations’.
The critical aspects related to the water supply infrastructure are (1) the unsatisfactory technical condition of the drinking water system and wastewater treatment systems, (2) the low percentage of the population with access to improved sanitation services, and (3) insufficient investment in the expansion and improvement of the water supply network and sanitation.
Difficulties in infrastructure development are related to design criteria and water and sanitation planning infrastructure tools, drinking water and wastewater quality monitoring programmes, and quality control in laboratories.
Local public authorities have the exclusive competency to set up, organise, coordinate and control the functioning of public utilities, as well as to create, manage and exploit public property assets in the urban infrastructure of the respective administrative territorial units.
Measures are needed to improve the operational and financial performance of water supply and sanitation service companies, in order to increase the safety and quality of services provided to the population through the elaboration and implementation of the short-, medium- and long-term development and maintenance of the public water supply and sanitation services. The integration of urban planning, spatial plans and socio-economic development programmes are of crucial importance in that context. These should also be supported by reviews by the local administrations to avoid duplicates in terms of roles and responsibilities and revisions of the regulations.
The poor condition of the water supply network and insufficient financial and technical resources are making it difficult to implement the desired conditions within the water supply system in the country. Water metering, the transparency of the water services, the monopoly of the water services and the lack of financial resources are the remaining challenges lying ahead in the water sector.
Indicator specification
Indicator definition
This indicator presents the volume of water supplied to the users by the water supply industry, taking into account water losses during transport and the population connected to the water supply industry, as a total and as a share of the total population.
Units
The total volume of water supplied by the water supply industry is measured in million cubic metres per year; the share of the total population connected to the water supply industry is provided as a percentage.
Rationale
Justification for indicator selection
The indicator is important for defining the level of development of water economy services and the degree of water accessibility to cover the needs of the population. The indicator also helps to identify trends in water supply in the country.
Scientific references
-
UNECE, 2014. Republic of Moldova –Environmental Performance Reviews – third review, United Nations Economic Commission for Europe, Environmental Performance Reviews Series No. 39, e-ISBN 978-92-1-056518, New York and Geneva.
-
UNECE, 2018. Guidelines for the Application of Environmental Indicators, Description of C5: Water supply industry and population connected to water supply industry.
-
UNECE, 2018. Guidelines for the Application of Environmental Indicators, Glossary of terms – C5: Water supply industry and population connected to water supply industry.
Policy context and targets
Context description
National policy context
Water Law No 272 of 23 December 2011, drawn up in accordance with the provisions of the European directives, aims to protect water against pollution and sets environmental quality standards (no online link has been provided).
Law No 303 of 13 December 2013 on the public service of water supply and sewerage regulates the unitary legal framework regarding the establishment, organisation, management, financing, operation, monitoring and control of the functioning of public drinking water and waste water sewage services (no online link has been provided).
Government Decision No 950 of 25 November 2013 on the approval of the regulation of the requirements for the collection, treatment and discharging of sewage into water bodies in urban and rural localities (no online link has been provided).
International policy context
Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 6 of the UN Sustainable Development Agenda for the period up to 2030 aims ‘to ensure access to water and sanitation for all’. Target 6.1 of SDG 6 is also aiming, ‘by 2030, to achieve universal and equitable access to safe and affordable drinking water for all’. Similarly, Target 6.4 states the aim to, ‘by 2030, substantially increase water use efficiency across all sectors and ensure sustainable withdrawals and supply of freshwater to address water scarcity and substantially reduce the number of people suffering from water scarcity’.
Targets
National targets
To ensure access to safe water and adequate sanitation for everyone in the country by 2028.
International targets
UN SDG 6, target 6.4: by 2030, substantially increase water use efficiency across all sectors and ensure sustainable withdrawals and supply of freshwater to address water scarcity and substantially reduce the number of people suffering from water scarcity.
Related policy documents
-
Water supply and sanitation strategy 2014-2028 of the Republic of Moldova. Government of the Republic of Moldova, 2014. Government decision No.199, 20 March 2014, Chisinau.
-
Sustainable Development Goals. UN (2016). Sustainable development goals, the sustainable development agenda.
Methodology
Methodology for indicator calculation
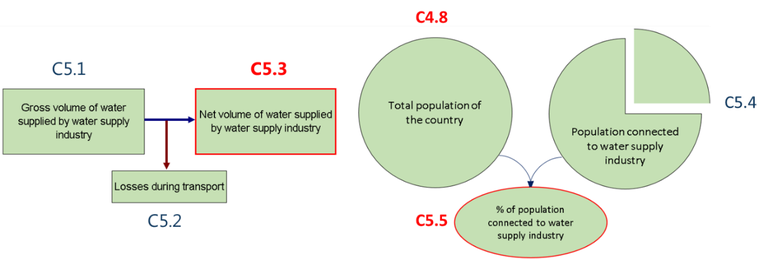
Note: Net volume of water supplied by the water supply industry = gross volume of water supplied by the water supply industry - losses during transport
Population connected to water supply industry (%) = population connected to water supply industry/total population of the country 100.
Units and equations
|
ID |
Component |
Units |
Equation |
|
C5.1 |
Gross volume of water supplied by water supply industry (ISIC 36) |
million m3/year |
|
|
C5.2 |
Losses during transport (ISIC 36) |
million m3/year |
|
|
C5.3 |
Net volume of water supplied by water supply industry (ISIC 36) |
million m3/year |
= C 5.1 - C 5.2 |
|
C4.8 |
Total population of the country |
million people |
|
|
C5.4 |
Population connected to water supply industry (estimation) |
million people |
|
|
C5.5 |
Population connected to water supply industry |
percentage (%) |
Methodology for gap filling
No gap filling has been performed.
Methodology references
-
EEA, 2005. EEA core set of indicators guide. EEA Technical report No 1/2005, ISBN 92-9167-757-4, Luxembourg.
-
UNECE, 2018. Guidelines for the Application of Environmental Indicators, Data template – C5: Water supply industry and population connected to water supply industry.
-
UNECE, 2018. Guidelines for the Application of Environmental Indicators, Description of C5: Water supply industry and population connected to water supply industry
-
UNECE, 2018. Guidelines for the Application of Environmental Indicators, Glossary of terms – C5: Water supply industry and population connected to water supply industry.
-
UNSD and UNEP, 2013. Questionnaire 2013 on Environment Statistics. United Nations Statistics Division and United Nations Environment Programme, Questionnaire 2013 on Environment Statistics, Section Water.
Uncertainties
Methodology uncertainty
No uncertainty has been specified.
Data sets uncertainty
No uncertainty has been specified.
Rationale uncertainty
No uncertainty has been specified.
Data sources
-
Losses during transportation provided by Statistical Databank of the National Bureau of Statistics of the Republic of Moldova
-
Population connected to water supply industry provided by Apele Moldovei of the Republic of Moldova under the ENI SEIS II East Project
-
The main indicator of water use provided by Statistical Databank of the National Bureau of Statistics of the Republic of Moldova

