C4 – Household water use per capita in the Republic of Armenia
Is household water use per capita decreasing in the Republic of Armenia?
Figure 1 - Development of total freshwater use by households in the Republic of Armenia (2000-2017)
Figure 2 - Development of household water use per capita in the Republic of Armenia (2000-2017)
Armenia is not a water-scarce country. On average (2000-2017), the annual renewable freshwater resource is around 6,800 million m3, corresponding to 2,200 m3/per capita per year. However, due to insufficient water management practices, Armenia has been facing severe water stress conditions for a long time. The annual water exploitation index (WEI) on average is higher than 40 %.
Water supplied to households is mainly used for drinking and cooking and for hygiene, including basic needs for personal and domestic cleanliness and amenity use such as car washing, lawn watering, etc. (Howard and Bartram, 2003).
In Armenia, the average annual total freshwater use is 2 549 million m3 for meeting the water demands of various sectors including households. In 2017, the total freshwater use by all sectors was around 2,040 million m3, of which 107.6 million m3 was water supplied by the water supply industry (5.2 %) to households.
Annual household water use has fluctuated tremendously in recent years, downwards from 2000 to 2009, and then upwards from 2009 to 2017 due to the expansion of the public water supply network to rural areas. By means of that improvement, the total water supplied to households by the water supply industry increased from 61.4 million m3 in 2009 to 107.6 million m3 in 2017. Over the same time, the population has decreased by 7 %.
Although drinking water demand is mostly met by groundwater resources in Armenia, water losses during transport remains high, with an average rate of 30 % of total water supply.
In 2017, on average, an Armenian citizen used 36 m3 of water from renewable freshwater resources. This corresponds to approximately 98.6 l of freshwater/capita per day.
According to the UNECE environmental performance assessment, during the 2000s, around 80 % of the pipes were more than 10 years old and 55 % were more than 20 years old.
Their maintenance had been neglected. The number of breakdowns was increasing regularly. However, since 2009, as a result of the implementation of the water management strategy of the Armenian government, the share of population connected to the water supply network has increased to 96.3 % of the total, with more focus being given to the rural areas.
Indicator specification
Indicator definition
The quantity of water used to cover the household and related utility needs of the population through the water supply industry and self-supply.
Units
Volumes of water used by households in total are measured in million cubic metres and per capita in cubic meter.
Rationale
Justification for indicator selection
The indicator is important for defining the level of development of the water economy services and the degree of water accessibility to cover all of the household needs of the population. The indicator also helps to identify trends in household water use in a particular country.
Scientific references
Government of the Republic of Armenia, 2014. Progressive Development Strategic Programme of the Republic of Armenia for 2014-2025. Government of the Republic of Armenia, 2014. Decision no. 442-N
Howard, G. and Bartram, J., 2003. Domestic Water Quantity, Service Level and Health. World Health Organization, WHO/SDE/WSH/03.02, Geneva, Switzerland.
UNECE, 2000. Environmental Performance Review- Armenia. United Nations Economic Commission for Europe, Committee on Environmental Policy, Environmental Performance Reviews Series No. 10, ISBN 92-1-116775-2, New York.
UNECE, 2018. Guidelines for the Application of Environmental Indicators, Description of C4: Household water use per capita.
UNECE, 2018. Guidelines for the Application of Environmental Indicators, Glossary of terms – C4: Household water use per capita.
Policy context and targets
Context description
National policy context
The law of the Republic of Armenia on the fundamentals of the national water policy is aimed at meeting the basic needs of the population, ensuring the maintenance and utilisation of renewable water resources and the quantity needed to reduce and prevent diseases due to water shortages and to maintain the aquatic ecosystems. In that context, the overall target is to satisfy the population’s everyday cultural and household water demands.
The progressive development of the strategic programme of the Republic of Armenia for 2014-2025 aims to increase the reliability and efficiency of the operation of the drinking water supply and sewage systems, reduce water losses and improve the quality of water and wastewater services.
International policy context
The UN SDG 6 of the Sustainable Development Agenda for the period up to 2030 is to ‘ensure access to water and sanitation for all’. Target 6.1 of SDG 6 aims ‘by 2030, to achieve universal and equitable access to safe and affordable drinking water for all’. Similarly, target 6.2 aims to, ‘by 2030, achieve access to adequate and equitable sanitation and hygiene for all and end open defecation, paying special attention to the needs of women and girls and those in vulnerable situations.’
Targets
No specific target has been identified.
Related policy documents
-
Progressive Development Strategic Programme of the Republic of Armenia for 2014-2025. Government of the Republic of Armenia, 2014. Decision no. 442-N
-
Republic of the Armenia Water Code (adopted on 4 June 2002)
-
Republic of Armenia Law on the National Water Programme (adopted on 27 November 2006)
-
Republic of Armenia Law on Fundamentals of the National Water Policy (adopted on 27 May 2005)
-
Sustainable Development Goals. UN (2016). Sustainable development goals, the sustainable
development agenda.
Methodology
Methodology for indicator calculation
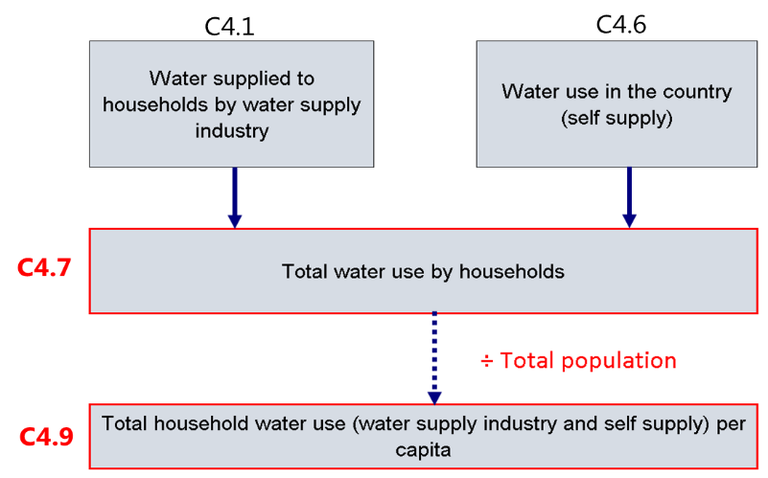
Note: Total water use per capita = total water use by households (water supplied to households by water supply industry + water use in the country (self-supply)/total population.
Units and equations
|
ID |
Component |
Units |
Equation |
|
C4.1 |
Water supplied to households by water supply industry |
million m3/year |
|
|
C4.2 |
Population connected to water supply industry (estimation) |
million persons |
|
|
C4.3 |
Water use per capita (water supply industry) |
m3/capita/year |
= C 4.1/C 4.2 |
|
C4.4 |
Population not connected to water supply industry (self-supply; estimation) |
million persons |
= C 4.8 - C 4.2 |
|
C4.5 |
Estimated water use by households supplied by self-supply per capita |
m3/capita/year |
|
|
C4.6 |
Water use in the country (self-supply) |
million m3/year |
= C 4.4 C 4.5 |
|
C4.7 |
Total water use by households |
million m3/year |
=C 4.1 + C 4.6 |
|
C4.8 |
Total population |
million persons |
|
|
C4.9 |
Total household water use (water supply industry and self-supply) per capita |
m3/capita/year |
=C 4.7/C 4.8 |
Methodology for gap filling
No gap filling has been performed
Methodology references
-
EEA, 2005. EEA core set of indicators guide. EEA Technical report No 1/2005, ISBN 92-9167-757-4, Luxembourg.
-
UNECE, 2018. Guidelines for the Application of Environmental Indicators, Data template – C4: Household water use per capita.
-
UNECE, 2018. Guidelines for the Application of Environmental Indicators, Description of C4: Household water use per capita.
-
UNECE, 2018. Guidelines for the Application of Environmental Indicators, Glossary of terms – C4: Household water use per capita.
-
UNSD and UNEP, 2013. Questionnaire 2013 on Environment Statistics. United Nations Statistics Division and United Nations Environment Programme, Questionnaire 2013 on Environment Statistics, Section Water.
Uncertainties
Methodology uncertainty
No uncertainty has been specified
Data sets uncertainty
No uncertainty has been specified.
Rationale uncertainty
No uncertainty has been specified.
Data sources
-
(C4)Household water use per capita by indicators and years provided by ArmStatBank

